Cancer is the name given to a collection of related diseases. In all types of cancer, some of the body’s
cells begin to divide without stopping and spread into surrounding tissues.
Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, human cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
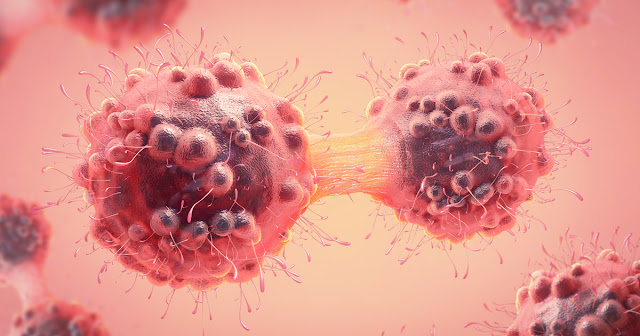
When cancer develops, however, this orderly process breaks down. As cells become more and more abnormal, old or damaged cells survive when they should die, and new cells form when they are not needed. These extra cells can divide without stopping and may form growths called tumors.
Many cancers form solid tumors, which are masses of tissue. Cancers of the blood, such as leukemias, generally do not form solid tumors.
Cancerous tumors are malignant, which means they can spread into, or invade, nearby tissues. In addition, as these tumors grow, some cancer cells can break off and travel to distant places in the body through the blood or the lymph system and form new tumors far from the original tumor.
Unlike malignant tumors, benign tumors do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues. Benign tumors can sometimes be quite large, however. When removed, they usually don’t grow back, whereas malignant tumors sometimes do. Unlike most benign tumors elsewhere in the body, benign brain tumors can be life threatening.
Differences between Cancer Cells and Normal Cells
Cancer/ cells differ from normal cells in many ways that allow them to grow out of control and become invasive. One important difference is that cancer cells are less specialized than normal cells. That is, whereas normal cells mature into very distinct cell types with specific functions, cancer cells do not. This is one reason that, unlike normal cells, cancer cells continue to divide without stopping.
In addition, cancer /cells are able to ignore signals that normally tell cells to stop dividing or that begin a process known as programmed cell death, or apoptosis, which the body uses to get rid of unneeded cells.
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body.These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread.[8] Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements.While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans.
Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths.Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol.Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants.
In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of a cell.
Typically, many genetic changes are required before cancer develops. Approximately 5–10% of cancers are due to inherited genetic defects
Cancer can be detected by certain signs and symptoms or screening tests
It is then typically furth investigated by medical imaging and confirmed by biopsy
The risk of developing certain cancers can be reduced by not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, eating plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, vaccination against certain infectious diseases, limiting consumption of processed meat and red meat, and limiting exposure to direct sunlight.Early detection through screening is useful for cervical and colorectal cancer. The benefits of screening in breast cancer are controversial. Cancer is often treated with some combination of radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Pain and symptom management are an important part of care. Palliative care is particularly important in people with advanced disease. The chance of survival depends on the type of cancer and extent of disease at the start of treatment
In children under 15 at diagnosis, the five-year survival rate in the developed world is on average 80%. For cancer in the United States, the average five-year survival rate is 66%.
Cancer cells may be able to influence the normal cells, molecules, and blood vessels that surround and feed a tumor—an area known as the microenvironment. For instance, cancer cells can induce nearby normal cells to form blood vessels that supply tumors with oxygen and nutrients, which they need to grow. These blood vessels also remove waste products from tumors.
Cancer cells are also often able to evade the immune system, a network of organs, tissues, and specialized cells that protects the body from infections and other conditions. Although the immune system normally removes damaged or abnormal cells from the body, some cancer cells are able to “hide” from the immune system.
Tumors can also use the immune system to stay alive and grow. For example, with the help of certain immune system cells that normally prevent a runaway immune response, cancer cells can actually keep the immune system from killing cancer cells.
ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق